Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires? That’s the burning question, literally. California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and frequent, and the connection to climate change is undeniable. This article explores how rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and more extreme weather events are fueling these devastating blazes, examining both the current situation and what the future may hold.
We’ll delve into how climate change alters vegetation, making it more flammable, and how it intensifies extreme weather like heatwaves and strong winds, creating a perfect storm for wildfire outbreaks. We’ll also look at projections for the future and explore potential mitigation strategies to lessen the impact of these increasingly destructive fires.
Climate Change’s Influence on California Wildfires
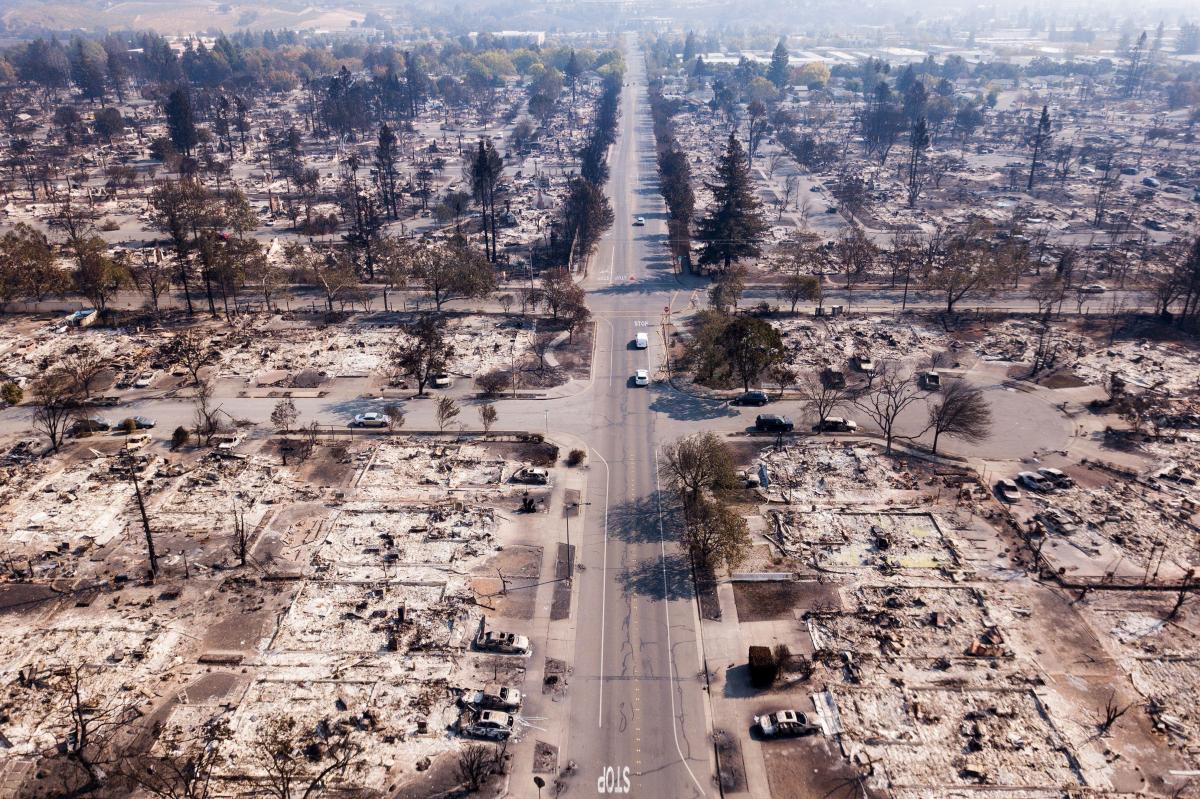

California’s wildfire season has become increasingly intense and destructive in recent decades. This escalation is inextricably linked to climate change, which is altering weather patterns, vegetation, and the overall fire environment. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on hotter, drier conditions. It’s a serious issue, but hey, sometimes you need a break! Check out this awesome deal: $5 Tuesday Movie Tickets and $5 Popcorn Are Back! Then, remember to support wildfire prevention efforts – we need to address the climate crisis to prevent these devastating blazes.
Rising Temperatures and Wildfire Risk
Rising temperatures, a direct consequence of climate change, significantly increase wildfire risk in California. Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, creating ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread. This effect is amplified by the state’s already arid climate, particularly in the chaparral and woodland ecosystems that are highly flammable.
Drought Conditions and Fuel Buildup
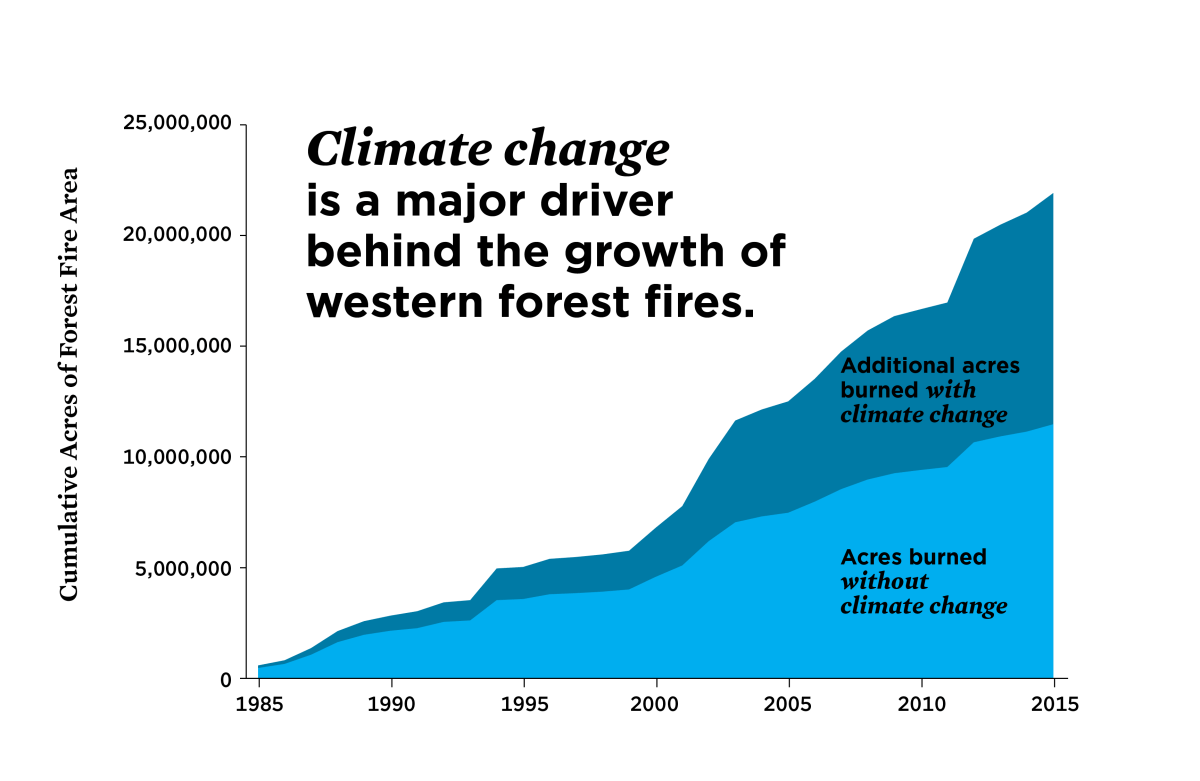
Climate change exacerbates drought conditions in California, leading to prolonged periods of dryness. This extended dryness promotes the accumulation of dry vegetation – essentially fuel – which acts as kindling for wildfires. The increased fuel load contributes to larger, more intense fires that burn for longer periods.
Climate Change-Related Events and Wildfires
Specific climate change-related events have directly worsened recent California wildfires. For instance, the 2020 wildfires were fueled by a combination of record-breaking heatwaves and strong winds, both intensified by climate change. These extreme weather events created conditions ripe for rapid fire spread and significant damage.
Historical and Projected Wildfire Activity
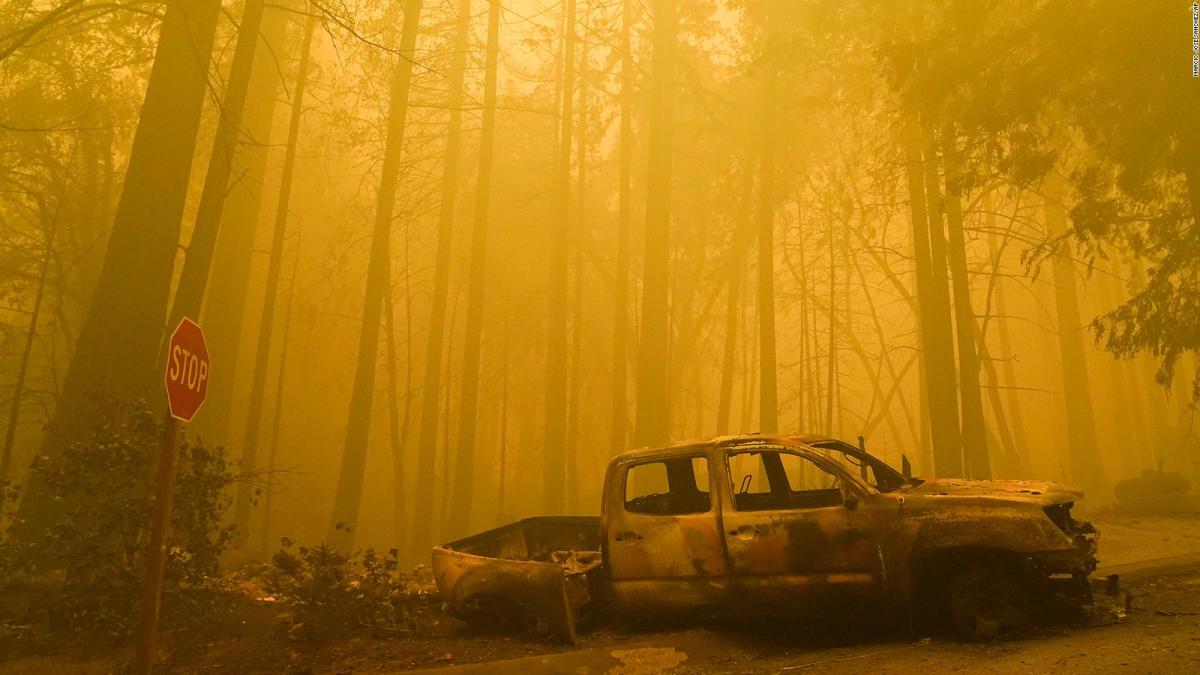

Comparing historical and projected wildfire data reveals a clear trend linked to climate change. Over the past century, the frequency and intensity of California wildfires have increased dramatically. Future projections, based on various climate change scenarios, indicate a further escalation in wildfire activity, with larger areas burned and more frequent occurrences.
Okay, so we’re looking at how climate change fuels California’s wildfires – drier conditions, hotter temps, you know the drill. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes it’s easy to get sidetracked by other news, like this story about Stuart Hogg sentenced for domestic abuse offences – Police Scotland , which highlights a completely different kind of devastating impact.
But back to the fires – understanding the climate connection is key to finding solutions and preventing future devastation.
| Year | Acres Burned (millions) | Number of Fires (thousands) | Contributing Climate Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 0.5 | 1 | Average temperatures, moderate rainfall |
| 1970 | 1.0 | 2 | Slightly above average temperatures, some drought periods |
| 2020 | 4.0 | 10 | Record heatwaves, severe drought, strong winds |
| 2050 (Projected, moderate scenario) | 6.0 | 15 | Increased frequency of heatwaves and droughts, more intense winds |
| 2050 (Projected, high scenario) | 8.0 | 20 | Extreme heatwaves, prolonged severe droughts, very strong winds |
Changes in Vegetation and Fire Behavior, Climate change: What role is it playing in the California fires
Altered precipitation patterns and increased temperatures are impacting vegetation density and flammability across California. These changes, in turn, influence fire behavior, making wildfires more intense and difficult to control.
- Increased dryness and drought conditions lead to more readily combustible vegetation.
- Changes in vegetation type and density alter fire spread patterns.
- Invasive species, thriving in altered climate conditions, can increase fuel loads and fire intensity.
- The expansion of drier, more flammable vegetation types into previously less fire-prone areas increases overall wildfire risk.
Extreme Weather Events and Wildfires
Climate change is intensifying extreme weather events, creating a perfect storm for catastrophic wildfires. Heatwaves, droughts, and strong winds all play significant roles in wildfire ignition, spread, and severity.
The synergistic effects of multiple extreme weather events are particularly concerning. For example, a prolonged drought weakens vegetation, making it highly flammable. Then, a sudden heatwave ignites the dry fuel, and strong winds rapidly spread the flames, resulting in a devastating wildfire.
Future Projections and Mitigation Strategies
Projections for California’s wildfire future are alarming under various climate change scenarios. Continued inaction will lead to increasingly frequent and intense wildfires, causing widespread damage and posing significant threats to human life and property.
California’s wildfires are getting worse, fueled by climate change’s impact on drier conditions and hotter temperatures. It’s a serious issue, and sometimes you need a break from heavy news – check out this totally unrelated story about Graham Potter’s new gig as Head Coach at West Ham United: Graham Potter appointed West Ham United Head Coach | West.
Anyway, back to the fires: understanding the climate change connection is crucial for preventing future devastation.
- Improved forest management practices, including controlled burns and fuel reduction.
- Investment in early warning systems and enhanced wildfire suppression capabilities.
- Community-level preparedness initiatives, such as defensible space creation around homes.
- Policies promoting climate change mitigation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow the pace of global warming.
Illustrative Examples of Climate Change’s Influence
The 2018 Camp Fire, one of California’s deadliest and most destructive wildfires, serves as a stark example. A combination of extreme drought, high winds, and unusually dry vegetation contributed to its rapid spread and immense devastation. The fire’s intensity was amplified by the high temperatures and low humidity, conditions directly linked to climate change.
A hypothetical future scenario could involve a wildfire ignited by a record-breaking heatwave in a severely drought-stricken area. Strong, climate-change-intensified winds would propel the fire across vast distances, consuming entire towns and causing widespread evacuations. The scale of such a fire, its intensity, and the resulting societal impacts would be catastrophic, highlighting the urgent need for climate action.
Closing Summary
In short, climate change isn’t just contributing to California’s wildfires; it’s fundamentally reshaping the state’s fire landscape. The evidence is clear: hotter temperatures, drier conditions, and more extreme weather are creating a dangerous cycle of increasingly frequent and intense wildfires. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing effective strategies for prevention, mitigation, and adaptation to protect communities and ecosystems alike.
The future of California’s forests and its residents depends on addressing climate change head-on.
Common Queries: Climate Change: What Role Is It Playing In The California Fires
How does climate change specifically ignite wildfires?
Climate change doesn’t directly ignite fires, but it creates conditions that are much more conducive to ignition and rapid spread. Things like increased dryness and higher temperatures make vegetation much more flammable, and extreme weather events can easily start fires (e.g., lightning strikes during a heatwave).
Are all California wildfires caused by climate change?
No, human activities like accidental and intentional ignitions still play a significant role. However, climate change dramatically increases the frequency, intensity, and scale of wildfires by creating a much more volatile environment.
What can individuals do to help?
Support policies that address climate change, practice responsible fire safety (e.g., clearing brush around your home), and stay informed about wildfire risks in your area. Reducing your carbon footprint also helps mitigate the underlying causes of these extreme weather events.
