How to operate a drone effectively and safely is more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to regulations, and developing skillful control. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and basic maneuvers to advanced techniques and emergency procedures. Whether you’re a novice eager to take flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to soar responsibly.
We’ll cover essential components, flight controls, camera operation, safety regulations, and troubleshooting tips, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable drone experience. Mastering the art of drone piloting requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application, and this guide aims to bridge that gap, providing a clear pathway to safe and proficient drone operation.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the individual parts of your drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of major components and provides a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
A drone comprises several key components working in concert. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust, efficiency, and noise.
- Motors: Electric motors drive the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. Brushless motors are common due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, responsible for processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates data from the IMU, GPS, and other sensors.
- Battery: Provides the power for all drone components. LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries are standard due to their high energy density and lightweight nature. Battery life is a critical factor in flight time.
- Camera: Captures aerial photos and videos. Features vary widely depending on the drone model, ranging from basic cameras to high-resolution, stabilized systems.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and autonomous flight features. It allows the drone to maintain its location and follow pre-programmed flight paths.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes. This data is crucial for stability and control.
- Remote Controller: Used to pilot the drone and control camera functions. It transmits signals wirelessly to the drone’s flight controller.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms enhances understanding and communication.
- Altitude Hold: The drone maintains a constant height above the ground.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera, reducing image shake and blurring.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, including the camera, battery, and any additional equipment.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that guides the drone back to its starting point.
- Flight Controller Firmware: The software that runs the flight controller, providing various functionalities and settings.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor, ensuring smooth and controlled flight.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see the drone’s perspective through a live video feed.
Drone Propeller Comparison
Different propellers are designed for various purposes, impacting performance characteristics.
| Propeller Type | Thrust | Efficiency | Noise Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow-spinning | Moderate | High | Low |
| Fast-spinning | High | Moderate | High |
| Carbon Fiber | High | High | Moderate |
| Plastic | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and legal drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone, calibrating sensors, and checking the battery.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow these steps:
- Visually inspect the drone for any damage to propellers, motors, or other components.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Confirm GPS signal lock and sufficient satellite connectivity.
- Review local airspace regulations and ensure you are operating within legal limits.
- Check weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or adverse weather.
- Ensure you have a clear line of sight to the drone at all times.
- Notify relevant authorities if required for your location.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Accurate calibration of the compass and IMU is vital for stable flight. Most drones have built-in calibration routines accessible through the remote control or dedicated software. Follow the manufacturer’s specific instructions for your drone model.
Battery Inspection and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial. Inspect the battery for any signs of damage, swelling, or leakage. Use only the manufacturer-recommended charger and avoid overcharging or discharging the battery completely.
Taking Off and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section details the procedures and techniques involved.
Safe Drone Takeoff
A smooth takeoff involves:
- Ensure the drone is in a level, open area away from obstacles.
- Power on the drone and controller, establishing a connection.
- Calibrate the compass if necessary.
- Initiate takeoff using the appropriate command on the controller (usually a lever or button).
- Ascend slowly and steadily, maintaining control at all times.
Controlled Drone Landing
A smooth landing ensures the drone’s safety and prevents damage.
- Slowly descend the drone, maintaining a steady rate of descent.
- Keep the drone level and stable during the descent.
- As the drone approaches the ground, reduce the descent rate further.
- Gently lower the drone to the ground, avoiding a sudden impact.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Unexpected situations may occur, requiring swift responses. For instance, if the drone starts drifting, gently counter the drift using the control sticks. If GPS signal is lost, initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) if available or carefully bring the drone down using visual cues.
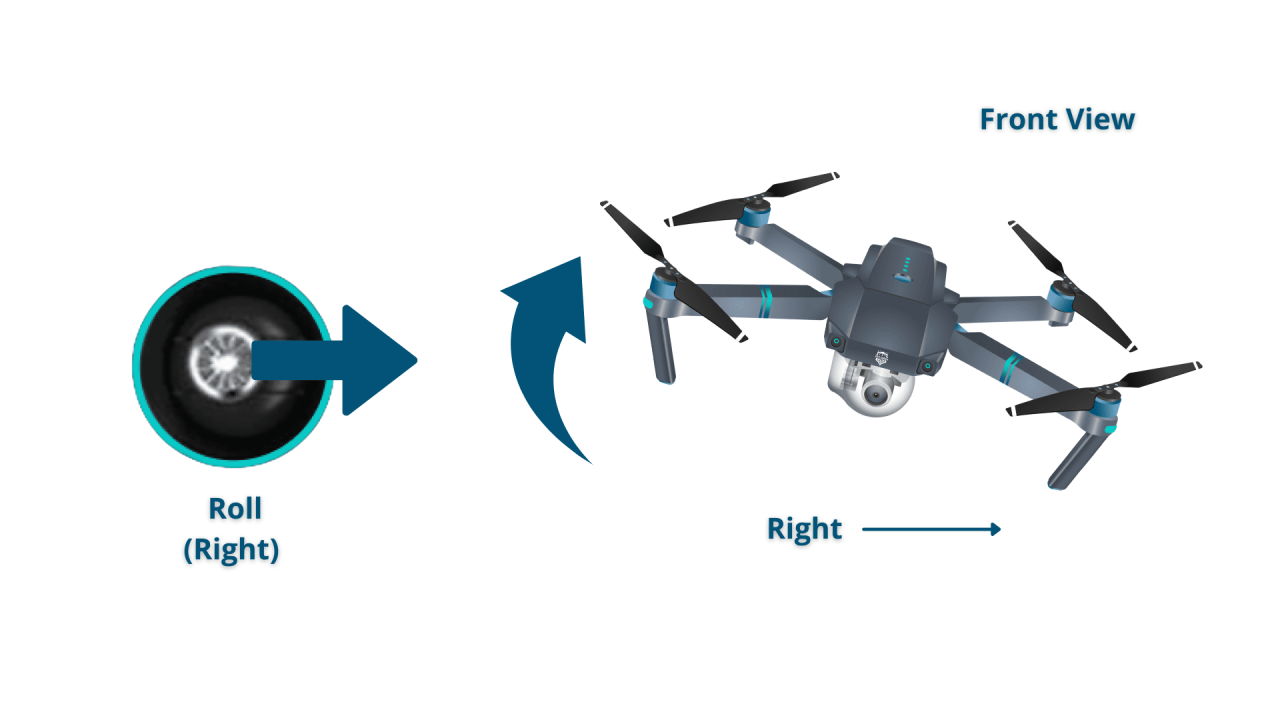
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the drone’s control system is essential for safe and effective flight. This involves learning the functions of the remote control and practicing basic maneuvers.
Remote Control Functions
Most drone remotes feature two control sticks and several buttons. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls forward/backward and sideways movement. Buttons usually manage functions like Return-to-Home (RTH), camera control, and flight mode selection.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers. GPS mode utilizes GPS data for improved stability and features like RTH.
Basic Flight Maneuvers Practice

Start with hovering, gradually progressing to controlled forward, backward, sideways movement, and turns. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area, gradually increasing speed and complexity as your skills improve.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and mastering composition techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like resolution, frame rate, and exposure can significantly impact image quality. Higher resolution yields larger files but requires more storage space. Higher frame rates result in smoother videos. Exposure settings control brightness and contrast.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
To capture high-quality aerial photos and videos, maintain a steady hand, avoid sudden movements, and utilize the drone’s stabilization features (if available). Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create visually compelling content.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Consider the “rule of thirds” and leading lines to create balanced and visually interesting compositions. Experiment with different perspectives, angles, and lighting conditions to capture unique and engaging aerial shots.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations and safety guidelines. This section Artikels crucial safety considerations and legal requirements.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly by location. Before flying, research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area, including airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations. Check with your local aviation authority for the most up-to-date information.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible and proficient drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Safety Considerations
Prioritize safety by always maintaining visual line of sight with your drone, avoiding crowded areas, and respecting airspace restrictions. Be aware of potential hazards like power lines, trees, and buildings. Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace without proper authorization.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
Potential hazards include:
- Loss of control: Practice in a safe environment and maintain a strong connection with the drone. Consider using features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Battery failure: Always use a fully charged battery and monitor the battery level during flight. Have a spare battery readily available.
- Collisions: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people. Use the drone’s obstacle avoidance features (if available).
- Adverse weather: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. Check the weather forecast before each flight.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
This section addresses common drone problems and provides solutions to help you resolve them efficiently.
Solutions for Common Drone Problems
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor failure. Low battery requires landing immediately and charging. GPS signal loss might necessitate landing in a safe area or using Return-to-Home (RTH). Motor failure often necessitates immediate landing and inspection for damage.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
Connectivity issues between the drone and controller can result from interference, distance, or low battery. Try moving to a location with less interference, checking battery levels, and restarting both devices.
Common Error Messages and Causes
| Error Message | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Battery is low on charge | Land immediately, charge battery |
| GPS Signal Lost | Weak GPS signal | Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky |
| Motor Failure | Motor malfunction | Inspect the motor for damage, replace if necessary |
| Connection Lost | Interference or distance | Move closer to the drone, restart devices |
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered basic flight, you can explore more advanced techniques such as waypoint navigation and automated flight.
Complex Maneuvers
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. Automated flight features such as orbit mode and follow-me mode offer creative possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
Flight Planning Software and Apps
Various software and apps are available for planning and executing complex drone flights. These tools allow you to create detailed flight paths, set waypoints, and control camera settings remotely.
Drone Flight Controller Comparison
Different flight controllers offer varying capabilities and features. Some prioritize stability and ease of use, while others focus on advanced features and customization options. Research and select a flight controller that aligns with your needs and skill level.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are essential for prolonging your drone’s lifespan and maintaining its optimal performance.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include:
- Inspecting propellers for damage and replacing them as needed.
- Cleaning the drone’s body and components to remove dirt and debris.
- Checking and tightening screws and connections.
- Inspecting the battery for damage and ensuring proper charging practices.
- Updating the drone’s firmware to the latest version.
Best Practices for Storage and Transportation
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use a protective case or bag during transportation to prevent damage.
Cleaning and Caring for Sensitive Components, How to operate a drone
Clean the camera lens gently with a microfiber cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Protect the drone’s sensors and other sensitive components from dust and moisture.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for handling low battery warnings, loss of control, and recovering a crashed drone.
Handling Emergency Situations
If a low battery warning appears, immediately begin a controlled descent and land the drone safely. If you lose control, attempt to regain control using the remote. If this fails, attempt to bring the drone down safely in a clear area. If all else fails, consider emergency procedures such as deploying a parachute (if equipped).
Recovering a Crashed Drone

Carefully inspect the drone for damage after a crash. Repair or replace damaged components before attempting another flight. If the damage is extensive, consider professional repair.
Emergency Scenario Flowchart
A flowchart would visually guide users through the appropriate steps for different emergency scenarios. This would depend on the specific situation, such as GPS signal loss, complete loss of control, or low battery. The flowchart would guide the user through prioritized steps, ensuring safety and efficient recovery procedures.
Operating a drone successfully involves a commitment to safety, understanding of technology, and adherence to regulations. By mastering the techniques and procedures Artikeld in this guide, you’ll not only gain proficiency in piloting your drone but also cultivate a responsible approach to aerial flight. Remember that continuous practice and a respect for airspace restrictions are key to becoming a skilled and safe drone operator.
Soar responsibly, and enjoy the incredible perspective that drone technology offers!
Essential Questionnaire
What is the ideal wind speed for safe drone operation?
Generally, winds below 15 mph are considered safe for most drones. However, always check your drone’s manufacturer specifications for wind tolerance.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (e.g., Attitude Mode) and carefully bring it down to a safe landing.
How long does a typical drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery capacity, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What is the best way to clean my drone’s camera lens?
Use a soft, microfiber cloth to gently wipe the lens. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
